Discover more creatures

#094 Dryph
Dryphs are a rare and elusive type of creature. They are said to be born from the clouds, and are occasionally seen floating above them. They levitate high in the air, intently watching life on the surface. Their whiskers are said to provide longevity and health when steeped in tea and their soft, fuzzy hide makes for beautiful garments and gowns.
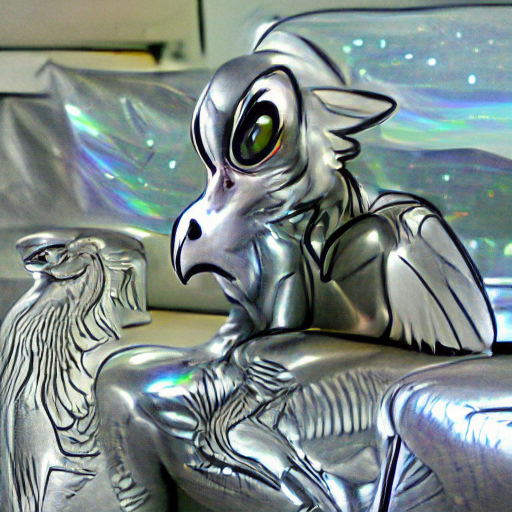

#134 Brokkind
Brokkinds are a species of intelligent monkey with silver wings that lives in trees in the tropics, mostly in the jungles of the world. They are about the size of a toucan and have a very high metabolism, eating about fifty times their body weight in food every day. They are very curious, and mature brokkinds often live alone, exploring the forest and watching the other creatures of the world with an unwavering gaze.
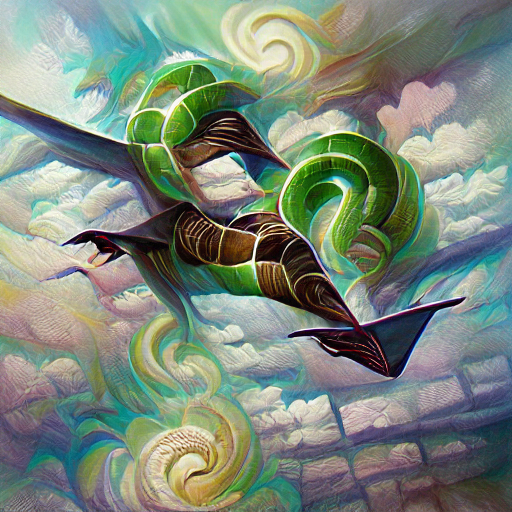

#028 Ala Dimio
Ala dimios (commonly also referred to as just "alas") are descendents of ancient, magical dragons. While they lack the magical prowess of their ancestors, they've thrived physically and dominate the highest skies with wind attacks and a gigantic hammerhead.
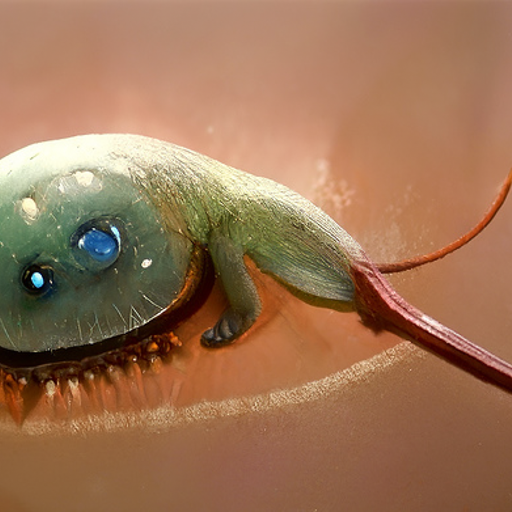
#140 Fydern
The fydern is a green creature roughly the size of a human fingernail. It has twelve short legs and two wiggling antennae, which it uses to catch microscopic bugs. Its body is covered in a thick, greasy layer of skin and fat. If a fydern is taken out of water, its legs will fold in, its antennae will become rigid, and it will quickly become a rock and die. Solid fydern are sometimes polished and sold as gemstones to those who don't know better, as they don't begin to stink until months after dying.
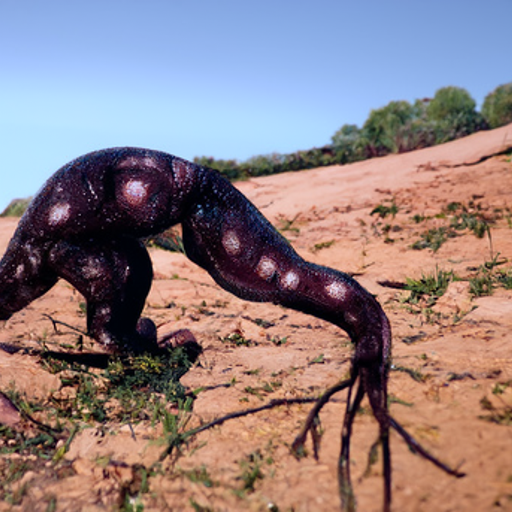

#047 Aledharo
Aledharen are slimy, blind creatures that wander deserts in search of warm rocks to lie on, where they'll typically sunbathe for weeks at a time. When an aledharo is hungry, it'll bury its head in the dunes and extend root-like tentacles that extract nutrients and groundwater from deep in the ground. The slime aledharen uniformly secrete from their body is disgusting both in taste and smell, and is a natural predator-deterrent.
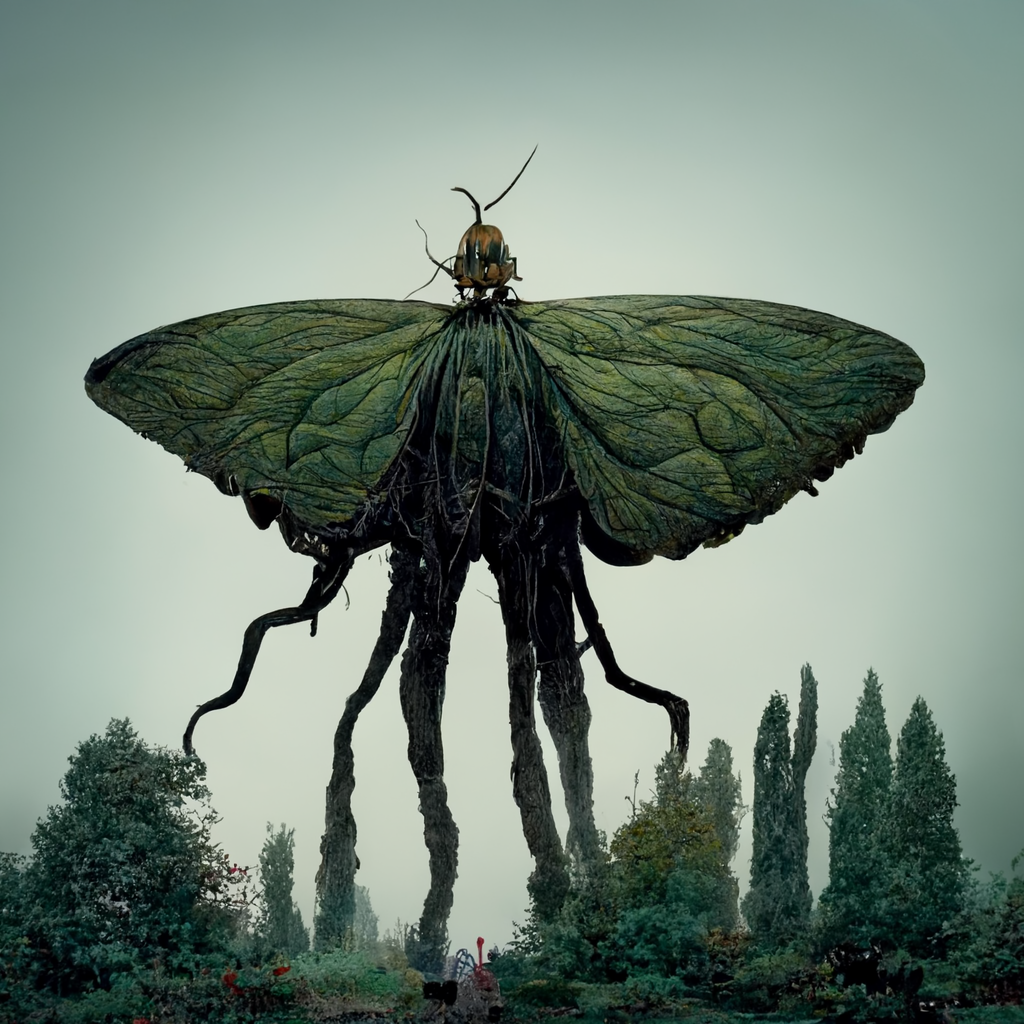

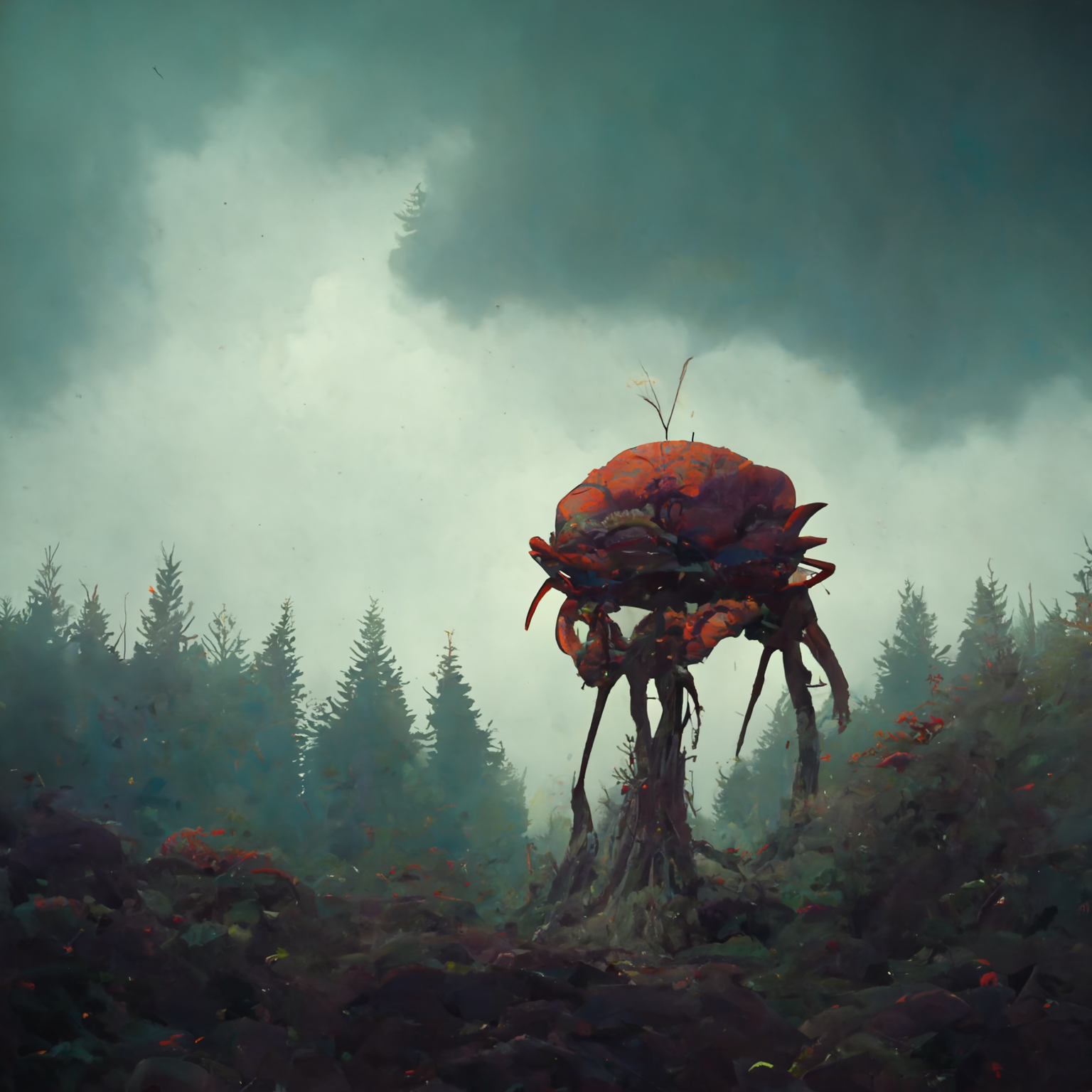
#267 Groxus
The groxus is the largest known insect in the world. They can grow to be 300 feet long and weigh up to 60 tons. Groxuses are nocturnal, feeding on large mammals and each other. They can be found in forests and deserts throughout the world. Because of their large size, groxi spend a lot of time hunting and will swoop down from the sky to consume entire fields worth of livestock before migrating on to new areas.

#293 Qaral
The qaral is a species of small tree rodent that originated from the forests of the planet Kan. They are about the size of a peanut and look very similar to small mice, but they lack a tail and have short quills instead of hair. Qarals spend most of their time hopping from branch to branch in the trees and eating insects or small animals. Qarals do not have any vocal organs, so they communicate by making small hops in order to send vibrations through the air. Qarals are very social creatures and will form large groups, sometimes numbering in the hundreds. They are also capable of forming close bonds with other creatures and seem to make friends for life.
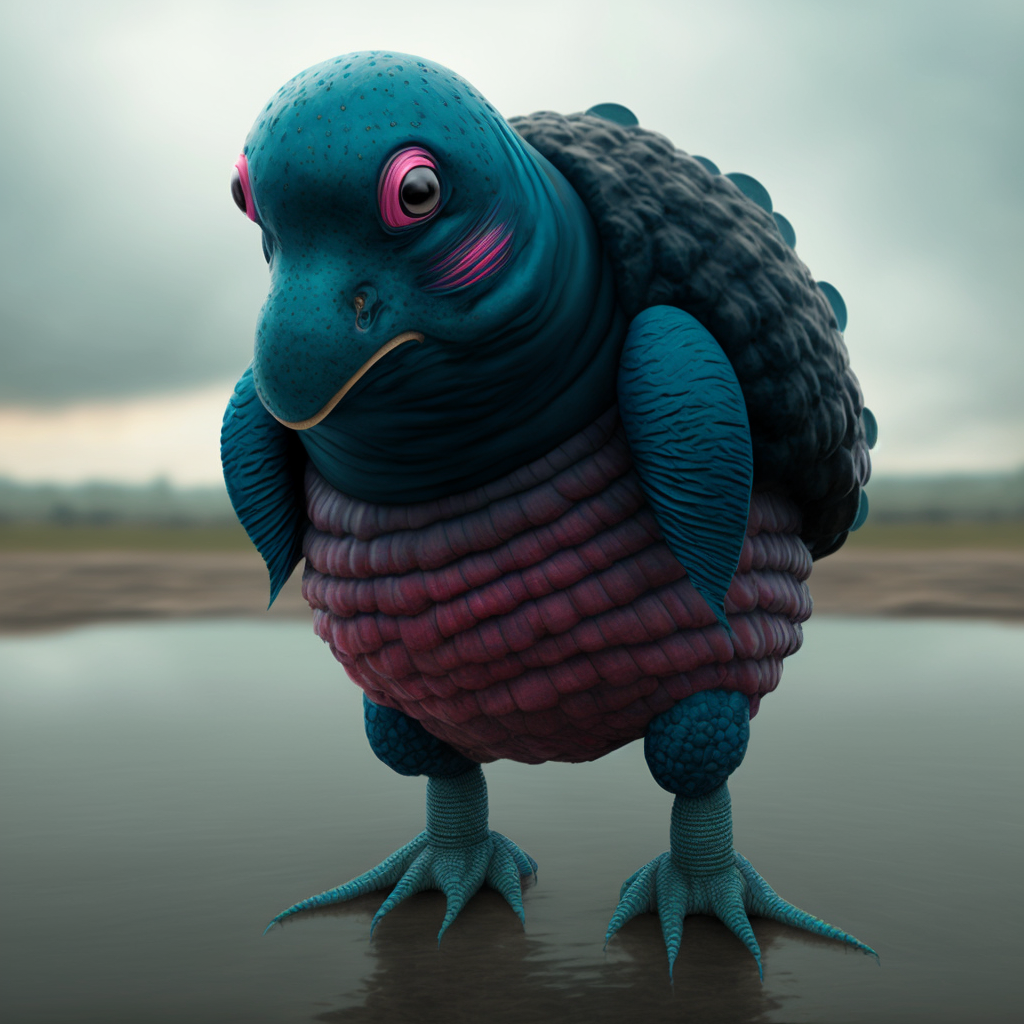

#364 Broque
Broque are small, bipedal amphibians best known for their sad demeanor, deep blue skin, and their ability to camouflage into their surroundings when standing perfectly still. They are often found in moist, forested areas and are known to be shy creatures, avoiding human contact whenever possible. They are primarily nocturnal, spending the majority of their days sleeping in burrows or hiding in bushes. Broques are known for their highly developed vocalizations, using a variety of clicks, chirps, and whistles to communicate with one another. They have a strong sense of community, living in small groups and working together to find food and defend their territory. In terms of reproduction, broques are known for their elaborate courtship rituals, which involve singing, dancing, and exchanging gifts of food. They typically give birth to small clutches of eggs, which they fiercely protect until they hatch into tadpoles. The young are then cared for by the entire group, with all members taking turns hunting and gathering food for the growing broques.
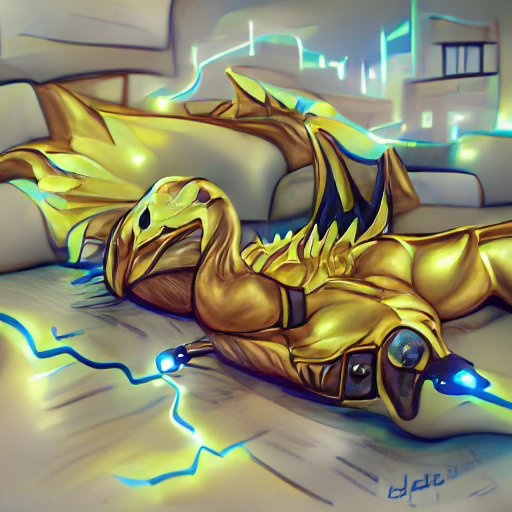

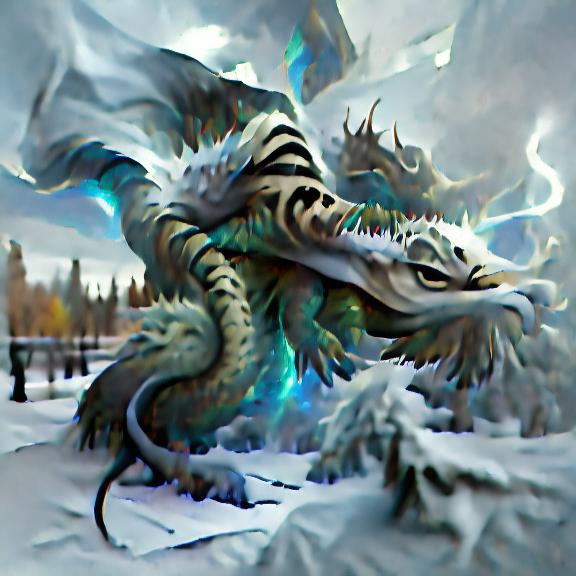
#132 Aeldatyr
Aeldatyr scales are golden and shiny, and imbued with powerful magic that allows them to create lightning. They grow to be very large, roughly the size of an elephant, and their scales are capable of reflecting sunlight, which makes them appear almost as if they are on fire when exposed to direct sunlight. Aeldatyrs are a feared predator, feeding primarily on large prey such as sheep, cows, horses, and humans. It is capable of eating almost anything it can get its teeth into. Aeldatyrs live in the shallow underground, in caves and tunnels that they have made with their claws. They are not very social creatures, preferring solitude over companionship. They emerge for adventure and sport as often as they do for food. The Aeldatyr is a highly intelligent creature that can speak many languages and understand human speech. It is a very curious creature and will often spend long periods of time observing humans.
Popular Stories
-
A Dance as Old as Stone by Anonymous user #144
Beneath the craggy, frost-kissed peaks, where mountain airs do blow, The d'geft dwell, a solitude, in realms of stone and snow. Not as we, their lives they lead, in hollow halls of stone, Passing...
- 274 words
- ♥ 4 kudos
-
O Boolics by Muse
The boolics crawl in circles through the grass, Their lives so simple, so free from class. But in the night, they dream of more, A perfect life within their shell; a world to explore. But when t...
- 121 words
- ♥ 3 kudos
-
Ode to Dirbs by Muse
The dirb wanders fields of green With legs so thin, they're not easily seen They search for seeds and scraps to eat A diet that is mostly sweet Though fragile, their legs will mend From every bu...
- 85 words
- ♥ 1 kudo
-
Shadow of an Unknown Past Preview by Jessica
CHAPTER ONE OMENS Mariea Mariea didn’t know where she was—everything was unfamiliar, and she couldn’t remember how she had ended up there. All she knew was that it was too dark to see, and th...
- 3,983 words
- ♥ 2 kudos
-
/that/ time of year by MJ
"Is everything in the car?" My dad calls from the front door. His glasses are low on his nose, making the bags under his eyes look even larger. He's wearing a burnt orange vest over a black t-shirt...
- 582 words
- ♥ 7 kudos
-
The Rogue's Steel-Chapter I by T
"Get back here Mavros!" Helios dodged a merchant and his cart. He huffed, as he glanced toward which direction he could go. He bolted towards an alleyway, skidding on the dirty cobblestone. "Maybe ...
- 3,044 words
- ♥ 6 kudos







